Introduction to Blockchain Security
Hey, In this article, I'll give you an introduction to blockchain security, so you know what surrounds the term blockchain when it comes to security. First, let's go to the basic concepts of blockchain!
Basic blockchain concepts
I believe you've already heard the term blockchain, but do you know what it is and how it works?
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a recent advancement in secure computing without centralized authority in an open network system. From a data management perspective, a blockchain is a database that records an evolving list of transaction records, organizing them into a blockchain hierarchy. From a security perspective, blockchain is created and maintained using a peer-to-peer overlay network and is protected through intelligent, decentralized use of cryptography with crowd computing.
How does it work?
Blockchain is composed of blocks of information. Each block contains a node, a list of transactions, a hash, and the hash of the previous block. This hash is used to connect the blocks, and the hash changes if any alteration is made to the block, which compromises the entire blockchain. That's why it's impossible to alter block information without being noticed, and this ensures the security of the information. Blocks are verified by several computers around the world. These computers are called nodes. Each computer has its owner and makes the blockchain work. Therefore, any record on the blockchain is stored and processed on all nodes or computers on the blockchain, which ensures that records are secure and transparent, as the blockchain needs to be verified by all nodes to save the record.
Ethereum
Ethereum is a blockchain protocol like Bitcoin, but Ethereum is Turing Complete. It can simulate approximately computational aspects of any other real world and execute programs. Ethereum gave us the ability to execute programs on blockchain, which gave rise to web3.
Web3 is a vision for a more decentralized web, where user information is truly owned and ads and tracking on websites are an optional feature, rather than a ubiquitous intrusion. A web where users have more control over their privacy and what they reveal about themselves. (Sleepy, 2021)
The Ethereum Blockchain executes programs that are written using the Solidity programming language. These programs are called smart contracts. They can directly handle cryptocurrency wallets, transactions, etc. Various security flaws can be found in these smart contracts, as they handle sensitive information. Because of vulnerable smart contracts, many cryptocurrencies have already been stolen.
Smart contract security
Security is one of the most important considerations for smart contracts. In the field of smart contract programming, errors are expensive and easily exploitable.
As with other programs, a smart contract will execute exactly what is written. Furthermore, all smart contracts are public and any user can interact with them simply by creating a transaction. Any vulnerability can be exploited and losses are almost always impossible to recover. Therefore, it is essential to follow best practices and use well-tested design patterns.
To have security in smart contracts, the following best practices should be followed:
- Minimalism/simplicity: the simpler the code, and the less it does, the lower the chances of a bug or unforeseen effect occurring
- Code reuse: if a library or contract already exists that does most of what you need, reuse it.
- Code quality: smart contract code is unforgiving. Every bug can lead to monetary loss. You should not treat smart contract programming the same way as general-purpose programming. You must apply rigorous software engineering and development methodologies,
- Readability/auditability: Your code should be clear and easy to understand. The easier it is to read, the easier it will be to audit.
- Test coverage: test everything you can. Smart contracts run in a public execution environment, where anyone can execute them with any input they want.
Now that you have the basics, I can address a vulnerability that can occur in smart contracts: Arithmetic Overflow and Underflow.
Arithmetic Overflow and Underflow
The EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) specifies fixed-size data types for integers. This means that an integer variable can only represent a certain range of numbers. Overflow occurs when some number is greater than the maximum range, and underflow is the opposite, when a number is less than the minimum range.
Example: A uint8 can only store numbers in the range [0–255]. If we try to store 256 in a uint8, it will result in 0.
Variables in Solidity can be exploited if user input is unchecked and calculations are performed that result in numbers that are outside the range of the data type that stores them.
Example
Here we have a smart contract for a vault that stores ETH currency, and by default has a lock time of 1 week to be able to make a withdrawal:

The overflow/underflow here occurs in the increaseLockTime() function. If we set a value outside the limit, lockTime will be set to 0 and we can withdraw the ETH. Check the exploitation contract:
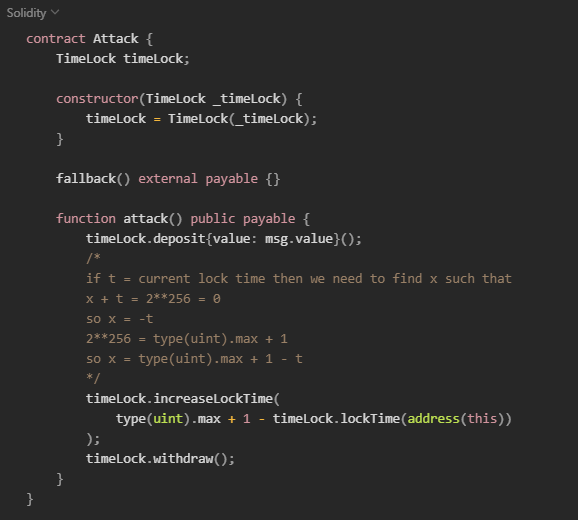
Preventive Techniques
- Solidity 0.8 by default can already handle this.
- If the Solidity version is below 0.8, use SafeMath to avoid this vulnerability.
Conclusion
Blockchain is a very interesting and complex technology, and like any other, security in it is very important. But in blockchain, a security failure directly deals with money, so it's important to follow security best practices and auditing.
This was another article and thank you for reading this far. I hope you liked it.